
Education Catalog
Our Education Catalog points you to more resources for in-depth plant and animal science as well as ecology and information on scientists.
Education Catalog

-Nelson Mandela
“Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world”
Animal Science
Step into the wild world of animal behavior – where survival strategies meet the quirks of nature!
Exploring the Diversity of Animal Life
Imagine a world where octopuses use tools, prairie dogs have a complex language to describe predators, and flamingos can only eat with their heads upside down. Welcome to the fascinating realm of animal science!
From the depths of the oceans to the highest mountain peaks, animals have evolved an impressive set of behaviors and adaptations. These aren’t just random actions – they’re sophisticated strategies for survival, communication, and thriving in diverse environments.
In animal science, we don’t just observe; we decipher nature’s code. We ask questions like:
- Animal Diversity: How did we end up with animals as different as jellyfish, eagles, and elephants? Explore the amazing variety of life forms and how they’re connected!
- Anatomy and Physiology: What makes a giraffe’s heart different from ours? How do polar bears stay warm in freezing temperatures?
- Animal Behavior: Why do elephants mourn their dead? How do arctic terns navigate their impressive 44,000-mile annual migration?
- Evolution and Adaptation: What purpose do a peacock’s colorful feathers serve, and how and why did this trait develop over time?
- Ecological Roles: How do keystone species like sea otters help maintain the balance in their ecosystems?
By studying animal classification and behavior, we gain insights into the world around us and how we interact.
Key Topics in Animal Science

Animal Diversity
The major animal groups and their characteristics
How animals are classified and why it matters

Animal Anatomy and Physiology
Body systems and how they function
How different animals are adapted to their environments

Animal Behavior
Understanding why animals behave the way they do
Communication, social structures, and survival strategies

Evolution and Adaptation
How animals have changed over time
Fascinating examples of evolutionary adaptations
Animals in Ecosystems
The roles animals play in their habitats
Predator-prey relationships and food webs

Did You Know?
The heart of a shrimp is located in its head!
Some animals, like axolotls, can regenerate lost body parts, including parts of their brain.
Explore Further
Curious about specific animal species? Dive into our detailed Animal Catalogs or our Animal Encyclopedia to learn more about your favorite creatures and discover new ones!
Test Your Animal Knowledge
Think you know animals? Put your skills to the test with our animal science quiz!
Plant Science
Discover the Amazing World of Plants!
Look around you – from the grass beneath your feet to the trees touching the sky, plants are everywhere. But there’s so much more to these green wonders than meets the eye. Did you know that trees can “talk” to each other underground? Or that some flowers create special partnerships with insects? There’s even a plant fast enough to catch its prey!
Welcome to the captivating world of plant science!
The plant kingdom has many kinds of different plants, ranging from tiny moss spores to giant sequoia trees. Through botany, the scientific study of plants, we uncover how these amazing life forms grow, adapt, and interact with their environment.
As we dive into plant science, we discover insights about:
- Plant Classification: How do scientists sort and group plants? Discover how we organize the plant kingdom from big groups down to individual species.
- Plant Diversity: How did we end up with plants as different as cacti, water lilies, and giant redwoods? Let’s learn about the variety of plant life and how they’re all related!
- Plant Structure and Function: How do trees transport water from roots to leaves hundreds of feet high? What makes some plants carnivorous?
- Photosynthesis: How do plants turn sunlight into food, and why is this process so important for all life on Earth?
- Plant Adaptations: How do desert plants survive with almost no water? Why do some flowers smell like rotting meat?
- Plants in Ecosystems: How do plants help create and maintain habitats for animals? What happens when we remove plants from an ecosystem?
By learning about these different parts of plant science, we can better understand how life on Earth works, how plants and animals depend on each other, and even find ways to help solve big problems like making sure everyone has enough food and protecting our planet.
Are you ready to explore the amazing world of plants? Let’s start our plant adventure and discover the wonders growing all around us!

Key Topics in Plant Science

Plant Structure and Function
Roots, stems, leaves, and flowers
How each part contributes to plant survival
Photosynthesis: Nature’s Power Plant
How plants convert sunlight into energy
Why photosynthesis is crucial for all life

Plant Adaptations
How plants survive in different environments
Fascinating examples of plant survival strategies

Plant Reproduction
From flowers to fruits: the plant life cycle
The role of pollinators in plant reproduction

Plants in Ecosystems
How plants interact with other organisms
The importance of plants in maintaining biodiversity

Did You Know?
The corpse flower (Amorphophallus titanum) can grow up to 3 meters tall and produces the largest unbranched inflorescence in the world. It’s famous for its pungent odor, which smells like rotting flesh to attract pollinators!!
Explore Further
Ready to dig deeper into the world of plants? Check out our detailed Plant Catalogs to learn about specific plant species and their unique characteristics.
Test Your Plant Knowledge
Think you’ve go a handle on plant basics? Try our fun plant science quiz!
Ecology
Explore Nature’s Connections!
Ecology is all about how living things interact with each other and their environment. It’s like studying a huge, living puzzle where every piece – from the tiniest bacteria to the largest whale – plays an important role. Through ecology, we learn how all these pieces fit together to create the amazing natural world around us.
As we dive into ecology, we learn fascinating insights about:
- Ecosystems: What makes up an ecosystem? How do different ecosystems work, from forests to oceans to deserts?
- Food Webs: Who eats whom in nature? How does energy move through living things in an ecosystem?
- Habitats: How do different plants and animals make their homes in nature? What happens when these homes change?
- Biodiversity: Why is having many different kinds of living things important? How does biodiversity help keep our planet healthy?
- Ecological Relationships: How do living things help or harm each other in nature? What are some surprising partnerships between different species?
- Human Impact: How do people affect the natural world? What can we do to help protect and preserve ecosystems?
By learning about these different parts of ecology, we can better understand how our planet works, why it’s important to protect nature, and how we can help keep Earth’s ecosystems healthy and balanced.
Key Topics in Ecology

Ecosystems
Different types of ecosystems around the world
How ecosystems function and their special adaptations
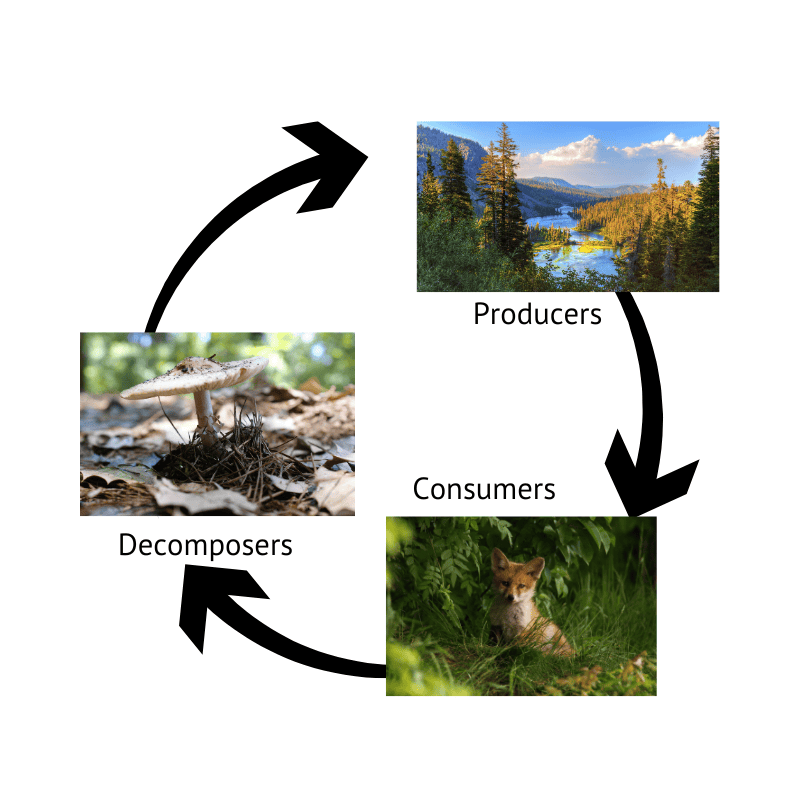
Food Webs and Energy Flow
How energy moves through an ecosystem
The roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers

Biodiversity
Why biodiversity is crucial for healthy ecosystems
Threats to biodiversity and conservation efforts

Ecological Relationships
Symbiosis, competition, and predation
How species depend on each other

Environmental Impacts
How changes in the environment affect ecosystems
Climate change and its ecological consequences

Did You Know?
A single teaspoon of soil can contain more living organisms than there are people on Earth!
The largest known living organism on Earth is a quaking aspen clone named Pando. It covers 106 acres and is estimated to be over 9,000 years old!
Explore Further
Want to see ecology in action? Check out our Ecology Page to learn how different species fit into their ecosystems!
Test Your Ecological Knowledge
Ready to put your ecosystem knowlege to the test? Try our ecology quiz!
Scientist Exploration
Meet the Curious Minds Behind Nature Science!
Welcome to the world of scientists who study plants, animals, and nature!
Scientists are like nature detectives. They ask questions, look for clues, and solve mysteries about the living world around us. From exploring deep oceans to climbing tall mountains, these curious people help us understand how nature works and why it’s so important.
As we learn about different scientists, we’ll discover:
- What Scientists Do: How do scientists study nature? What tools and methods do they use to learn about plants and animals?
- Famous Nature Explorers: Who are some of the most important scientists in history? What big discoveries did they make?
- Modern-Day Researchers: What are scientists studying today? How are they using new technology to learn about nature?
- Different Types of Scientists: What kinds of scientists study living things? How are plant scientists different from animal scientists?
- Becoming a Scientist: What does it take to become a nature scientist? What skills do you need, and what kind of education is helpful?
- Science in Action: How do the things scientists learn help us in our everyday lives? How does their work help protect nature?
By learning about these different types of scientists, we can see how exciting it is to study the living world. We’ll understand how scientific discoveries happen and why the work of scientists is so important for our planet.
Are you ready to meet some amazing scientists and learn about their adventures in nature?
Featured Scientists
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
- Field: Evolution and Natural Selection
- Key Contribution: Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
- Fun Fact: Darwin was an avid beetle collector in his youth!
Jane Goodall (1934-present)
- Field: Primatology and Anthropology
- Key Contribution: Groundbreaking studies of chimpanzee behavior
- Fun Fact: She was the first scientist to observe tool use in chimpanzees
E.O. Wilson (1929-2021)
- Field: Entomology and Biodiversity
- Key Contribution: Pioneered the field of sociobiology and was a world-leading expert on ants
- Fun Fact: He was nicknamed “the ant man” for his extensive work on ant behavior and ecosystems
Sylvia Earle (1935-present)
- Field: Marine Biology and Oceanography
- Key Contribution: Pioneering research on marine ecosystems and advocacy for ocean conservation
- Fun Fact: Known as “Her Deepness,” she set a women’s depth record for suit diving and has led over 100 expeditions
Alexander von Humboldt (1769-1859)
- Field: Biogeography and Ecology
- Key Contribution: Laid the groundwork for our understanding of ecosystems
- Fun Fact: He described the human-induced climate change two centuries ago!
Rosalind Franklin (1920-1958)
- Field: X-ray Crystallography and Molecular Biology
- Key Contribution: Critical work on the molecular structures of DNA, RNA, viruses, coal, and graphite
- Fun Fact: Her X-ray diffraction images of DNA were key to discovering its double helix structure
Scientist Spotlight
Each month, we feature a different scientist, past or present. Check out our current spotlight:

When Dr. Cassandra Quave enters a forest, she doesn’t just see trees and flowers – she sees potential medicines waiting to be discovered. As a leading ethnobotanist, she combines traditional knowledge about plant remedies with cutting-edge science to find new ways to fight disease. Her work bridging ancient plant wisdom with modern medical challenges has positioned her at the forefront of the search for solutions to antibiotic resistance, one of today’s most pressing health threats.
Known for her resilience and determination, Dr. Quave has overcome personal challenges to become a pioneering researcher whose work spans continents and cultures. Her discoveries from plants like the European chestnut are opening new pathways to combat dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria, potentially saving countless lives in the process.
Scientist Profile
- Name: Dr. Cassandra Quave
- Field: Ethnobotany and medicinal plant research
- Education:
- Ph.D. in Biology with focus on ethnobotany from Florida International University
- Bachelor’s degree in Biology and Anthropology from Emory University
- Early life and inspiration:
- Cassandra Quave grew up with a congenital condition that led to the amputation of her right leg below the knee as a child. This experience helped shape her resilience and determination. “I never set out to become an ethnobotanist,” Dr. Quave often shares. “I was pre-med with plans to become a surgeon.” Her path changed during an undergraduate research experience in the Amazon rainforest, where she witnessed indigenous communities using local plants for medicine and recognized the untapped potential of these botanical remedies.

“The plants that heal us have been right under our noses all along. We just need to remember how to see them.”
– Dr. Cassandra Quave
Notable Works and Achievement
Major Contributions
- Identified compounds from the European chestnut that can disarm MRSA (a dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria) without killing it, potentially avoiding the problem of developing resistance
- Published over 100 scientific papers on medicinal plants and their compounds
- Established a massive extract library containing thousands of plant samples for testing against pathogens
- Co-founded PhytoTEK LLC, a drug discovery company focused on plant-based solutions to antibiotic resistance
- Authored “The Plant Hunter: A Scientist’s Quest for Nature’s Next Medicines,” a memoir about her research journey
Awards and Honors:
- Received prestigious grants from the National Institutes of Health and Department of Defense
- Serves as Curator of the Emory Herbarium
- Leads the Quave Research Group at Emory University
- Created the first free online Botanical Medicine course available to the public
- Named among the “Women Who Shape Science” by the National Geographic Society
Impact on the Field
Relevance:
Dr. Quave’s work has transformed how scientists approach antibiotic resistance. Rather than following the conventional path of finding compounds that kill bacteria directly, she searches for substances that disrupt bacterial communication or disable their ability to cause disease. This novel approach may help overcome the cycle of resistance that has rendered many antibiotics ineffective.
Legacy:
Beyond her scientific discoveries, Dr. Quave has become an important voice for preserving both biodiversity and cultural knowledge about plants. Her fieldwork documenting traditional remedies helps preserve generations of botanical wisdom that might otherwise be lost. By demonstrating the medical value of these traditions, she makes a powerful case for habitat conservation and the protection of indigenous knowledge.
Personal Insights
Challenges Overcome:
After earning her PhD, Dr. Quave faced significant obstacles getting funding for her unconventional approach to antibiotic research. “Many colleagues thought looking at traditional plant remedies was outdated,” she explains. “But I believed these plants held secrets that could help address modern medical problems.” Her persistence eventually paid off, and her lab now leads the field in discovering plant compounds that work differently than conventional antibiotics.
Her personal experience with disability has also informed her perspective. “Living with a disability taught me to be creative in solving problems,” she has noted in interviews. “That same creativity helps me see potential in plants that others might overlook.”
“Get comfortable being uncomfortable. Whether you’re hiking through thorny brush to collect plants, learning a new language to interview traditional healers, or mastering complex laboratory techniques, this field demands versatility and perseverance.”
–Dr. Cassandra Quave’s advice to aspiring botanists
Conclusion
Dr. Cassandra Quave represents the exciting future of botanical medicine research. By bridging traditional knowledge with modern science, she’s uncovering plant compounds that could help solve one of healthcare’s most pressing challenges. Her work reminds us that sometimes ancient wisdom contains the seeds of solutions to our most modern problems.
Her career demonstrates the value of interdisciplinary thinking and the importance of preserving both biological and cultural diversity. For aspiring scientists interested in plant science, Dr. Quave offers an inspiring example of how curiosity, persistence, and openness to different ways of knowing can lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
For those interested in learning more about medicinal plants, check out Dr. Quave’s free online Botanical Medicine course or her memoir, “The Plant Hunter,” which details her journey from curious student to pioneering researcher.


Scientist Exploration
Review past scientist spotlights.
Inspired by these scientists? Learn about careers in life sciences.
Let us know what type of education and/or resources you would like us to provide for you.
We are always looking for your input to make the resources better.
